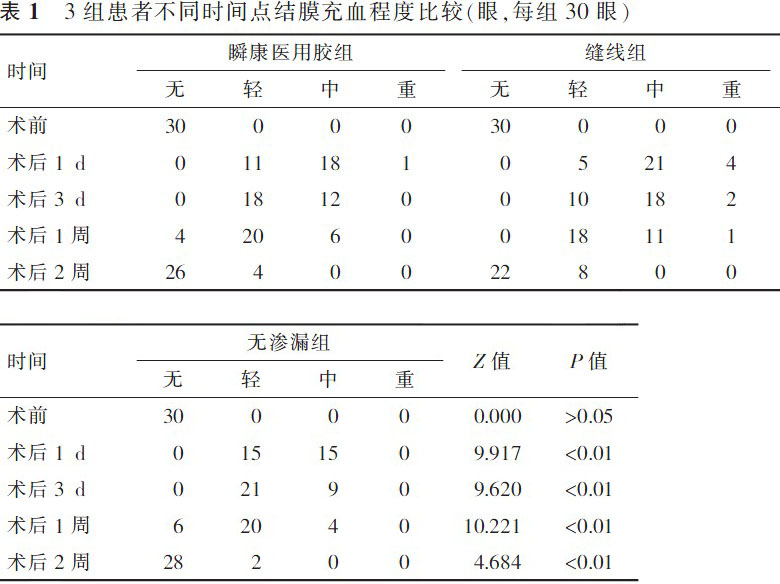
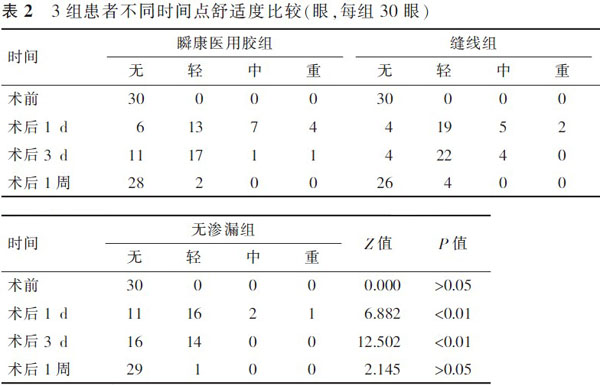
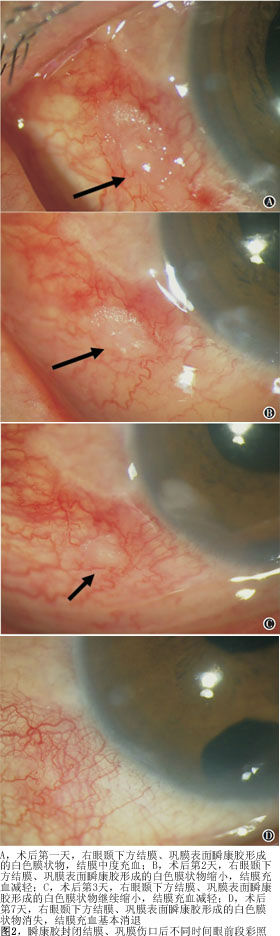
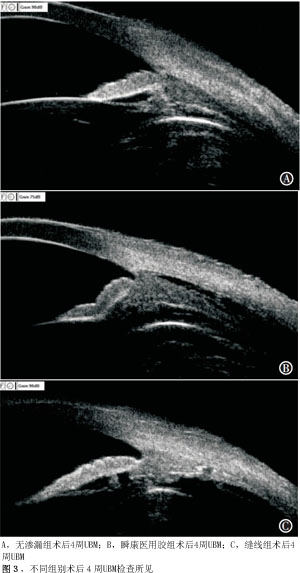
【摘要】 目的 寻找一种无创、安全有效、简单的方法预防23G微创玻璃体手术后早期低眼压的发生。方法 前瞻性对照研究。将2011年7月至2012年9月在徐州市眼病防治研究所行23G微创玻璃体手术的连续病例资料分为3组:术中无巩膜切口渗漏未予缝合为无渗漏组,有巩膜切口渗漏者按照随机数字表法分为瞬康胶组(用α-氰基丙烯酸烷基酯医用胶封闭伤口)、缝线组(用8-0缝线缝合巩膜切口),每组30例。用卡方检验比较各组间术后早期低眼压的发生率,用秩和检验比较各组结膜充血程度、患者舒适度、最终随访视力的差异。结果 3组术后1周内发生低眼压的情况:缝线组无低眼压发生,瞬康胶组、无渗漏组分别有1例(3%)、4例(13%)发生低眼压,3组差异具有统计学意义(χ2=6.291,P<0.05)。3组患者在术后1 d(Z=9.917,P<0.01)、3 d(Z=9.620,P<0.01)、1周(Z=10.221,P<0.01)时结膜充血程度差异具有统计学意义,无渗漏组最轻,缝线组最重。3组患者在术后3 d时术眼疼痛程度差异具有统计学意义(Z=12.502,P<0.01),无渗漏组最轻,缝线组最重。3组患者术后2个月时视力进行比较差异无统计学意义(Z=4.234,P>0.05)。3组在术后2周、4周用超声生物显微镜检测均未发现切口内有纤维组织内生。结论 应用α-氰基丙烯酸烷基酯医用胶或缝线封闭渗漏的巩膜切口能够有效地预防23G微创玻璃体手术后早期低眼压的发生。其中α-氰基丙烯酸烷基酯医用胶具有无创、安全有效、使用简便等优点。
【关键词】 玻璃体手术,23G; 低眼压; α-氰基丙烯酸烷基酯医用胶
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-845X.2014.02.013
基金项目:江苏省卫生厅科研基金资助项目(H201054)
作者单位:221000 徐州市眼病防治研究所
通信作者:李甦雁
Email:lisuyan1226@126.com
A study of the prevention of scleral incision leakage after 23-gauge minimally invasive vitrectomy
Li Suyan, Liu Sha, Zhang Zhengpei, Ji Sujuan, Liu Haiyang. Eye Institute of Xuzhou, Xuzhou 221000, China
Corresponding author:Li Suyan,Email:lisuyan1226@126.com
【Abstract】 Objective To find a non-invasive, safe, effective, and simple method to prevent the occurrence of early hypotony after 23G vitrectomy. Methods Using a prospective, controlled study, 90 patients who met hospital standards for 23G vitrectomy underwent surgery in Eye Institute of Xuzhou from July 2011 to September 2012. Patients were divided into three groups of 30 patients each. No-leakage group had no wound leakage. Those who had wound leakage were divided further into 2 groups based on treatment approach: Suncon medical adhesive group, whose scleral incisions were coated with an α-cyanoacrylate medical adhesive, and suture group, whose incisions were sutured with an 8-0 absorbable suture. All surgeries were performed by the same surgeon. Early postoperative hypotony, conjunctival hyperemia, postoperative comfort level, and scleral incision healing were compared among the three groups. A chi-square test and rank sum test were used. Results Occurrence of hypotony was evaluated for all three groups 1 week after surgery: no hypotony occurred in the suture group while the no-leakage group and Suncon medical adhesive group had 1 and 4 cases of hypotony, respectively. The differences in rates of hypotony among the three groups were statistically significant (χ²=6.291, P<0.05). The differences in postoperative occurrence of conjunctival hyperemia among the three groups at 1 day (Z=9.917, P<0.01), 3 days (Z=9.620, P<0.01), and 1 week (Z=10.221, P<0.01) were all statistically significant. Congestion occurred the least in no-leakage group and was the worst in suture group. At day 3 postoperatively, the pain and discomfort of patients in the three groups were significantly different (Z=12.502, P<0.01). Discomfort was the least in the no-leakage group and was the worst in the suture group. BCVA improved in all groups 2 months after surgery (Z=4.234, P>0.05). Abnormal fibrous ingrowth was not detected at the sclerotomy sites with ultrasound biomicroscopy. Conclusion It was demonstrated that the use of an α-cyanoacrylate medical adhesive or suture to close scleral incision leakage in 23G vitrectomy is effective in preventing early hypotony. The former is noninvasive and feasible and provides a better approach.
【Key words】 Vitrectomy,23G; Hypotony; α-cyanoacrylate medical adhesive