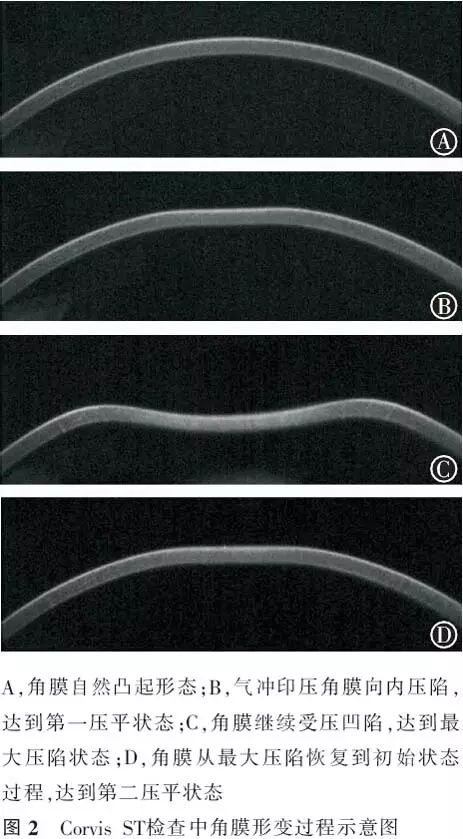
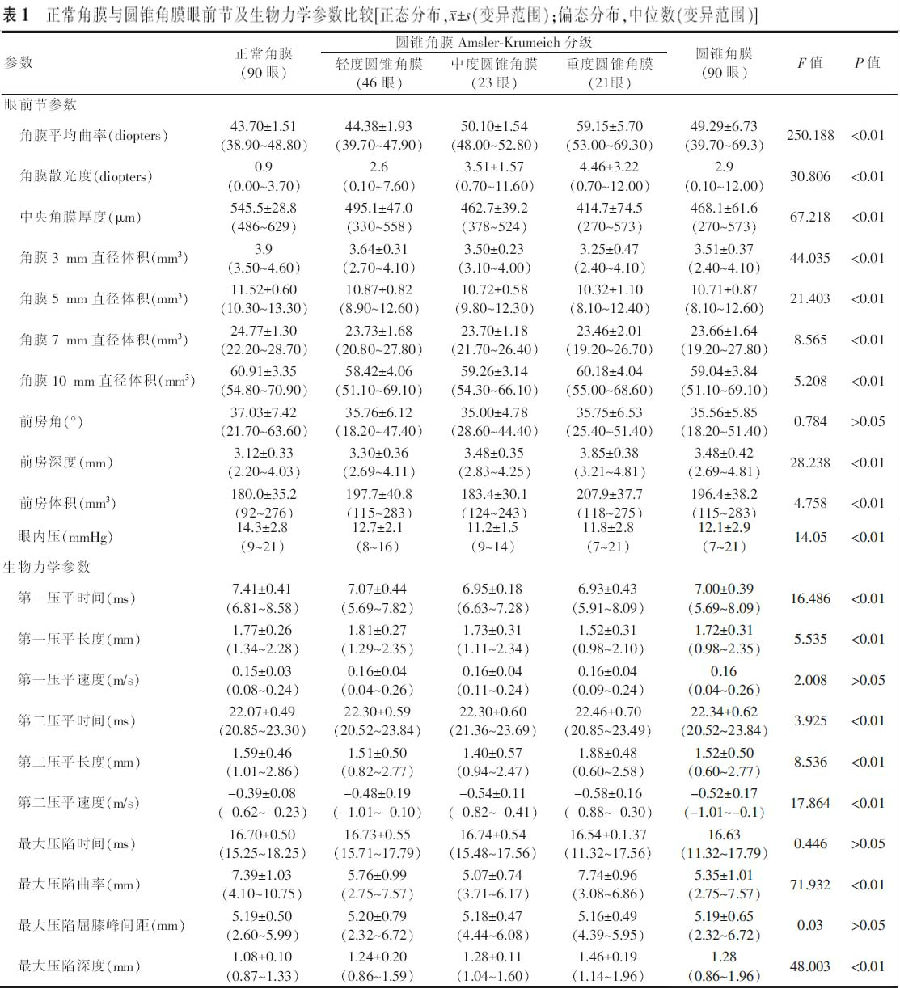
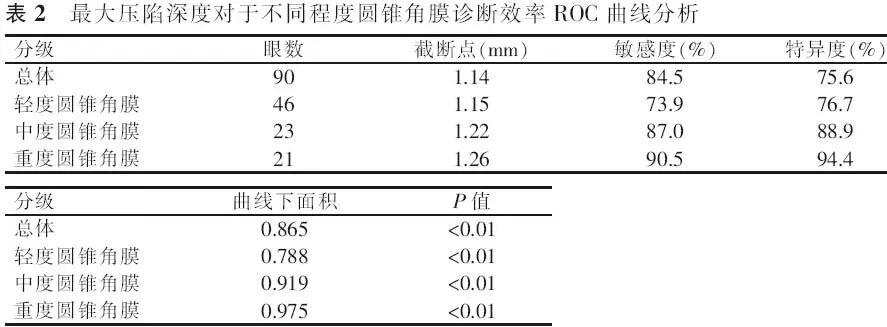
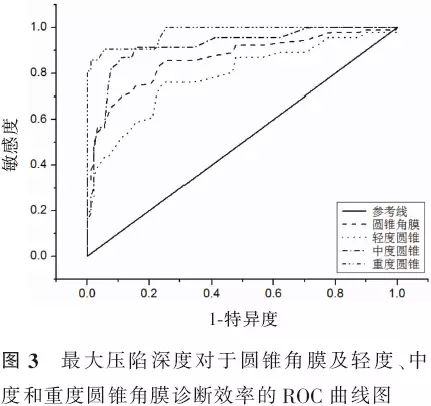
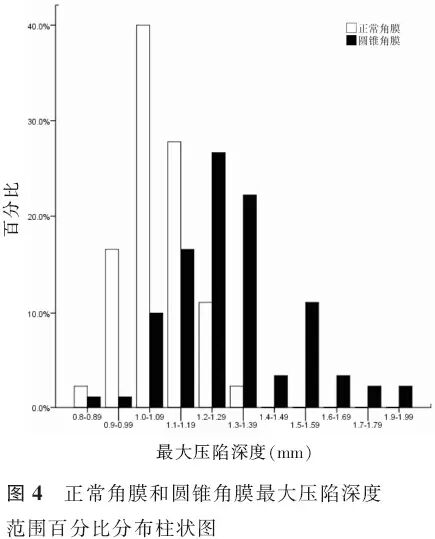
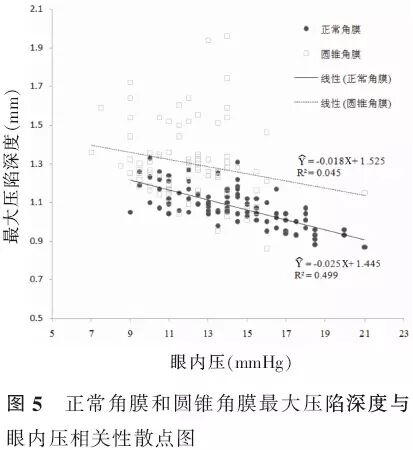
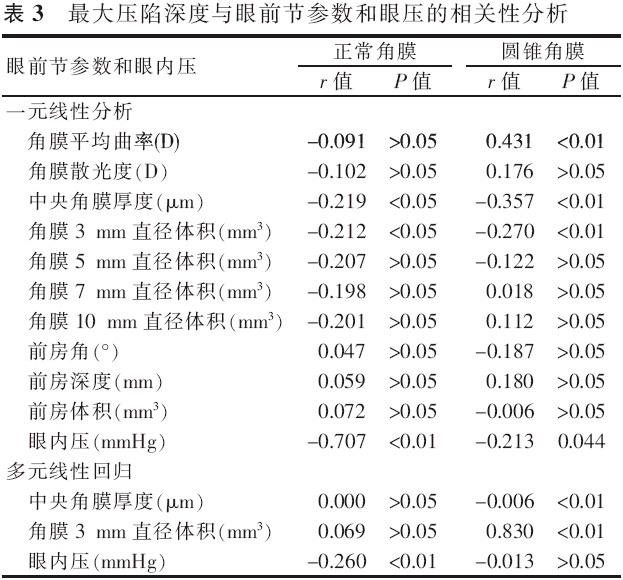
【摘要】 目的 应用可视化角膜生物力学分析仪(Corvis ST)比较圆锥角膜和正常角膜的生物力学特征,探讨角膜生物力学参数在圆锥角膜诊断中的作用及其相关影响因素。方法 病例对照研究。选取圆锥角膜患者65例(90眼)(圆锥角膜组),并按照Amsler-Krumeich分级法分为轻度圆锥角膜46眼、中度圆锥角膜23眼和重度圆锥角膜21眼;选取正常角膜对照者90例(90眼)作为正常角膜组。分别应用Pentacam眼前节分析系统测量眼前节形态参数;应用Corvis ST测量角膜生物力学参数。采用独立样本t检验、Wilcoxon秩和检验、ANOVA、非参数检验对比各组眼前节形态参数及生物力学参数并分析各参数间的相关性,绘制受检者工作特征(ROC)曲线。结果 除前房角、第一压平长度、最大压陷时间和最大压陷屈膝峰间距外,圆锥角膜组其余眼前节形态参数和角膜生物力学参数与正常角膜组均有明显差异。ROC曲线分析显示,所测量的生物力学参数中,角膜最大压陷深度对于圆锥角膜的诊断效率最高(曲线下面积0.865、敏感度84.5%、特异度75.6%、截断点1.14 mm),并且随着圆锥角膜严重程度的升级其诊断效率逐渐提高。在2组中角膜最大压陷深度与眼内压、中央角膜厚度和角膜中央3 mm内体积呈负相关(正常角膜组和圆锥角膜组,眼内压:r=-0.707、-0.213;中央角膜厚度:r=-0.219、-0.357;角膜中央:3 mm内体积r=-0.212、-0.27;P值均<0.05)。结论 Corvis ST能够有效测量角膜生物力学特征,其测量参数中角膜最大压陷深度对于圆锥角膜具有诊断意义,但其与眼内压和角膜厚度呈负相关,临床应用中需特别注意相关影响因素。
【关键词】 生物力学; 圆锥角膜; 可视化角膜生物力学分析仪; 最大压陷深度
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-845X.2014.05.003
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(81271052)
作者单位:100853 北京,中国人民中国人民
通信作者:黄一飞,Email:huangyf301@gmail.com
Assessment of corneal biomechanical properties using corneal visualization Scheimpflug technology at different stages of keratoconus
Tian Lei, Wang Liqiang, Meng Xiaoli, Wu Ying, Huang Yifei. Department of Ophthalmology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China
Corresponding author:Huang Yifei,Email:huangyf301@gmail.com
【Abstract】 Objective To compare the corneal biomechanical properties of the corneas of keratoconic eyes and normal eyes using corneal visualization Scheimpflug technology (Corvis ST), and to investigate the role of corneal biomechanical parameters in the diagnosis of keratoconus. Methods Ninety keratoconic eyes from 65 patients and 90 normal eyes from 90 participants were enrolled in this comparative study. Based on the Amseler-Krumeich keratoconus stages, the keratoconic eyes were divided into a mild group (46 eyes), moderate group (23 eyes) and severe group (21 eyes). Tomography and biomechanical parameters of all eyes were obtained with the Pentacam and Corvis ST, respectively. All parameters were compared between the keratoconic and normal groups. The correlation between deformation amplitude and anterior segment parameters was also analyzed. An independent t test,Wilcoxon rank sum test, ANOVA,nonparameter test were used. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to distinguish keratoconus from the normal cornea. Results The tomography and biomechanical parameters of the keratoconic eyes were significantly different from those of normal eyes except for the anterior chamber angle,first applanation length,highest concavity time,and peak distance. The deformation amplitude (area under the curve: 0.865)was the best predictive parameter,with a sensitivity of 84.5%, specificity of 75.6% and cut-off point of 1.14 mm. The diagnostic efficiency of the deformation amplitude increased with an increase in the severity of keratoconus. In both the normal and keratoconic groups, the deformation amplitude was negatively correlated with intraocular pressure, central corneal thickness,and corneal volume at 3 mm. The respective r values of the deformation amplitudes of the normal and keratoconic groups in regard to:intraocular pressure,-0.707 and -0.213;central corneal thickness,-0.219 and -0.357;and corneal volume at 3 mm,-0.212 and -0.27. All P values were <0.05. Conclusion Corvis ST offers an alternative method for measuring corneal biomechanical properties. The deformation amplitude has a high sensitivity for the diagnosis of keratoconus. The negative correlations with intraocular pressure and central corneal thickness deserve clinical attention.
【Key words】 Biomechanics; Keratoconus; Corneal visualization Scheimpflug technology; Deformation amplitude