Episcleritis
表层巩膜炎
Symptoms
Acute onset of redness and mild pain in one or both eyes, typically in young adults; a history of recurrent episodes is common. No discharge.
Signs
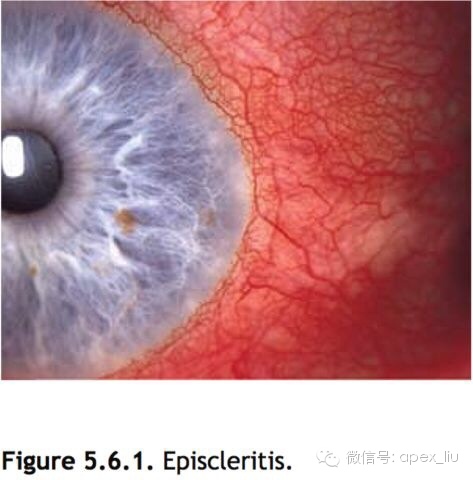
(See Figure 5.6.1.)
症状:单眼或双眼眼红和轻度疼痛,急性发作,多发生于年轻人,易复发,无分泌物。
体征:见图5.6.1.
Critical. Sectoral (and, less commonly, diffuse) redness of one or both eyes, mostly due to engorgement of the episcleral vessels. These vessels are large and run in a radial direction beneath the conjunctiva.
Other. Mild to moderate tenderness over the area of episcleral injection or a nodule that can be moved slightly over the underlying sclera may be seen. Fluorescein staining can sometimes be seen over the nodule. Associated anterior uveitis and corneal involvement are rare. Vision is normal.
主要体征:
单眼或双眼眼红,呈扇形或弥漫性(较少见),主要是由表层巩膜血管充血造成,这些巩膜血管粗大,在结膜下呈放射状走行。
其他体征:
表层巩膜充血区域轻中度触痛,有些病例可见到能被轻轻推动的巩膜结节。有时可见巩膜结节的荧光素着染。少有前葡萄膜炎和角膜受累并发。视力正常。
Differential Diagnosis
•\tScleritis: Typically older patient. May have known underlying immune-mediated disease (e.g., collagen vascular disease). Pain is deep, severe, and often radiates to the ipsilateral side of the head or face. The sclera may have a bluish hue when observed in natural light. Scleral (and deep episcleral) vessels, as well as conjunctival and superficial episcleral vessels, are injected. The scleral vessels do not blanch on application of topical phenylephrine 2.5%. Possible corneal involvement with adjacent stromal keratitis. See 5.7, Scleritis.
•\tIritis: Cells and flare in the anterior chamber. May be present with scleritis. See 3.5, Traumatic Iritis and 12.1, Anterior Uveitis (Iritis/Iridocyclitis).
•\tConjunctivitis: Diffuse redness and discharge with follicles or papillae. See 5.1 Acute Conjunctivitis and 5.2, Chronic Conjunctivitis.
鉴别诊断:
1.巩膜炎 多为老年患者。可有原发的免疫系统疾病,如胶原血管性疾病。疼痛较重,部位较深,常放射到同侧头面部。自然光下巩膜呈淡蓝色。巩膜和深表层巩膜血管、球结膜和浅层的表层巩膜血管充血。局部给予2.5%去氧肾上腺素巩膜血管不变白。可伴有毗邻的角膜基质炎。参见本章第七节巩膜炎。
2.虹膜炎 前房可见细胞和闪辉,可伴发巩膜炎。参见第三章第五节外伤性虹膜炎和第十二章第一节前葡萄膜炎(虹膜炎/虹膜睫状体炎)。
3.结膜炎 弥漫性眼红和分泌物,伴有滤泡或乳头增生。参见本章第一节急性结膜炎和第二节慢性结膜炎。
•\tContact lens overwear or tight contact lens syndrome. May be reaction to contact lens solution. Must be considered in all contact lens wearers. See 4.21, Contact Lens–Related Problems.
(overwear,中文版的翻译,可能不准确)
4.角膜接触镜过度磨损或者角膜接触镜过紧综合征 可能是角膜接触镜清洁液造成的不良反应。所有的角膜接触镜戴用者均可发生。患者对接触镜不耐受、有睡眠时戴接触镜史、或长期佩戴不合适的接触镜。参见第四章第二十一节角膜接触镜性眼病。
Etiology
•\tIdiopathic: Most common.
•\tInfectious: e.g., herpes zoster virus (scars from an old facial rash may be present, may cause episcleritis or scleritis).
•\tOthers: e.g., rosacea, atopy, and thyroid disease.
病因学:
1.特发性 最常见。
2.感染性 如带状疱疹病毒感染。可见陈旧性面部皮疹造成的瘢痕,可引起表层巩膜炎或巩膜炎。
3.结蹄组织病 如类风湿性关节炎、结节性多动脉炎、系统性红斑狼疮、Wegener肉芽肿。
4.痛风 血尿酸水平增高。
5.其他 感染性肠道疾病,酒渣鼻,特应性和甲状腺疾病。
对照这一段的原文和中文版,会发现中文版有增加的内容。
但是,请看第六版的原文。)
Etiology
Idiopathic: Most common.
Infectious: Herpes zoster virus (scars from an old facial rash may be present, may cause episcleritis or scleritis) and others.
Others: Rosacea, atopy, collagen vascular diseases, gout, and thyroid disease.
Work-Up
1 History: Assess for a history of rash, arthritis, venereal disease, recent viral illness, other medical problems.
2 External examination in natural light: Look for the bluish hue of scleritis.
3 Slit-lamp examination: Anesthetize (e.g., topical proparacaine) and move the conjunctiva with a cotton-tipped applicator to determine the depth of the injected blood vessels. Evaluate for any corneal or anterior chamber involvement. Check IOP.
4 Place a drop of phenylephrine 2.5% in the affected eye and reexamine the vascular pattern 10 to 15 minutes later. episcleral vessels should blanch, highlighting any underlying scleral vascular engorgement.
5 If the history suggests an underlying etiology, or in cases with multiple recurrences, the appropriate laboratory tests should be obtained [e.g., antinuclear antibody (ANA), rheumatoid factor, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), serum uric acid level, RPR, FTA-ABS, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)].
检查:
1.病史 有无皮疹、关节炎、性病病史,最近有无病毒感染和其他的内科疾病。
2.自然光下的外眼检查 观察有无巩膜炎造成的巩膜蓝色变。
3.裂隙灯检查 表面麻醉下,用棉签推动球结膜,观察血管充盈的深度。检查有无角膜或前房的受累,测眼压。(如果单纯为了检查结膜推动,从而判断充血层次,不一定需要表麻,直接用眼睑推动结膜即可。)
4.患眼滴一滴2.5%去氧肾上腺素,10-15min后观察,表层巩膜血管应收缩变白,使其下方的巩膜血管充血清晰可见。
5.如患者的病史提示有原发病因,或在多次复发的病例,需做相应的实验室检查如抗核抗体(ANA)、类风湿因子、血沉(ES)、血尿酸水平、快速血浆反应素、螺旋体抗体吸附荧光测定(FTA-ABS)、抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体(ANCA)。
(复发病例,是深入检查的指证)
Treatment
1 If mild, treat with artificial tears (e.g., Refresh Tears) q.i.d.
2 If moderate to severe, a mild topical steroid (e.g., fluorometholone 0.1% q.i.d., loteprednol 0.5% q.i.d.) often relieves the discomfort. Occasionally, more potent or frequent topical steroid application is necessary.
3 Oral NSAIDs may be used as an alternate steroid-sparing initial therapy (e.g., ibuprofen 200 to 600 mg p.o., t.i.d. to q.i.d., or naproxen 250 to 500 mg p.o., b.i.d. with food or antacids).
治疗:
1.轻度 使用人工泪液 如Refresh Tears,日4次。
2.中、重度 可应用较温和的类固醇眼液,如0.1%-0.25%氟米龙,日4次,或0.5%氯替泼诺(露达舒),日4次,以缓解不适。有些病例需应用强效的类固醇滴眼或频繁滴用类固醇。
3.治疗伊始,口服非甾体抗炎药可用于节制激素治疗,如布洛芬200-600mg,日3-4次,或萘普生250-500mg,日2次,饭中服用或与抗酸剂同服。
Note
Some physicians prefer oral NSAIDs to topical steroids as initial therapy.
注:
有些医师建议开始治疗时采用口服非甾体抗炎药而非局部用类固醇。
Follow-Up
Patients treated with artificial tears need not be seen for several weeks unless discomfort worsens or persists.
If topical steroids are used, recheck every 2 to 3 weeks until symptoms resolve. The frequency of steroid administration is then tapered.
Patients are informed that episcleritis may recur in the same or contralateral eye.
随访:
1.使用人工泪液治疗的患者数周之内不必复查,除非病情加重或经久不退。
2.眼局部应用类固醇的患者每2-3周复查1次,直至症状缓解。然后类固醇滴眼的频率逐渐减少。
3.告知患者表层巩膜炎可在同一眼或对侧眼上复发。