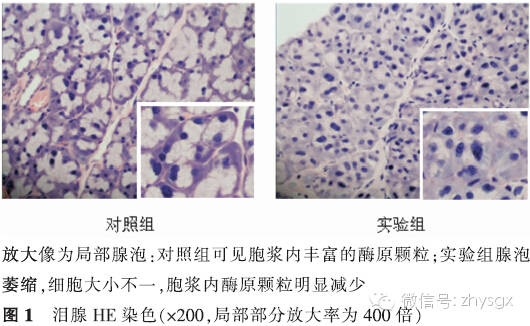
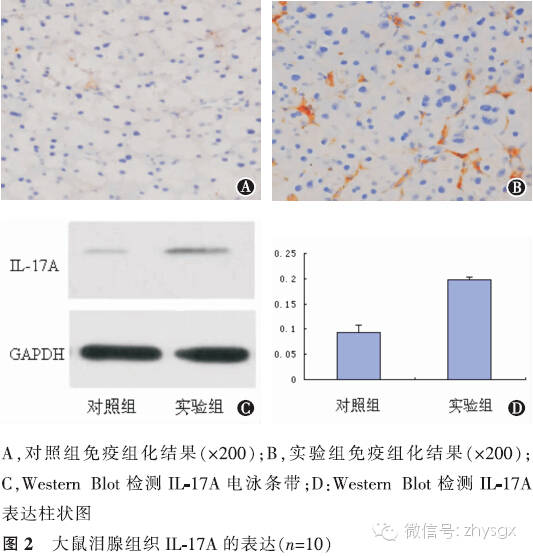
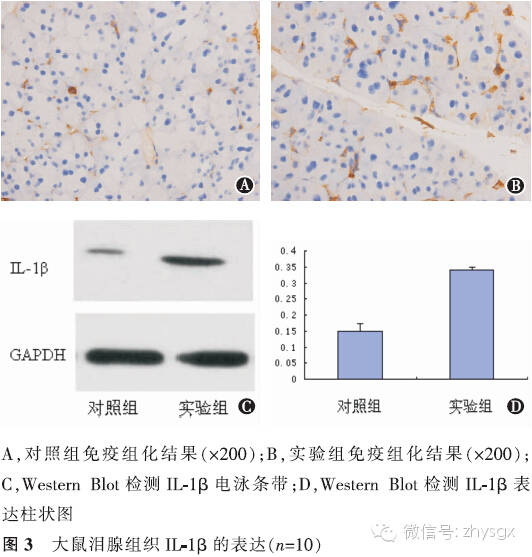
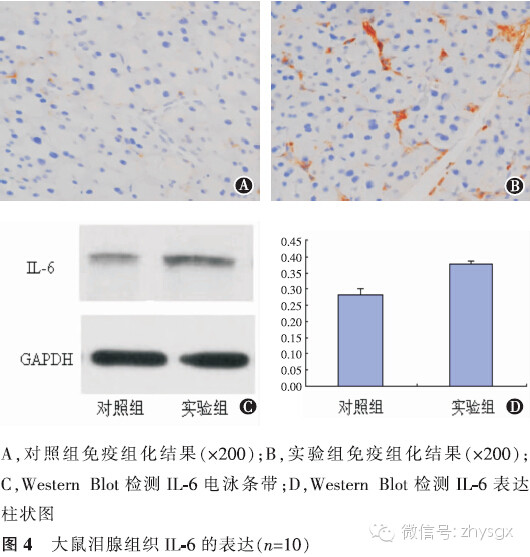
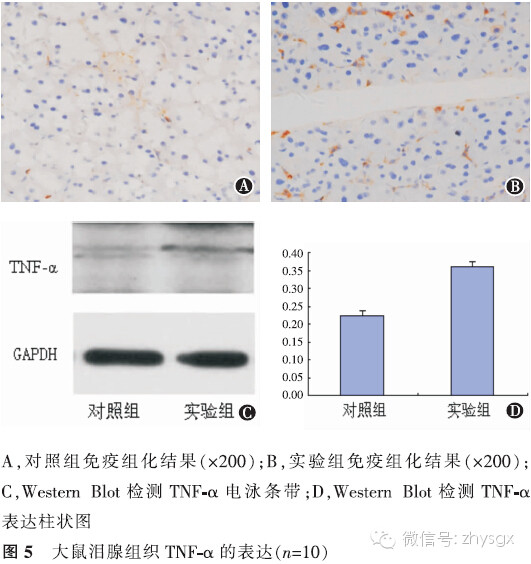
【摘要】 目的 建立去卵巢大鼠模型,观察性激素水平改变对泪腺中IL-17A以及IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α等炎症因子表达的影响。方法 实验研究。健康雌性SD大鼠20只随机分为2组,实验组(10只)摘除大鼠双侧卵巢,对照组(10只)为未摘除卵巢的模拟手术组。术前及术后第1个月、第2个月、第3个月时2组均行泪液分泌试验(SIT)、角膜荧光染色检查进行眼表评估。于第3个月时放射免疫分析法分别检测2组大鼠血清雌二醇、睾酮含量,HE染色观察泪腺上皮细胞形态,免疫组化染色法、Western Blot法检测2组泪腺中IL-17A、IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的表达。2组性激素质量浓度比较、炎症因子A值表达比较均应用独立样本t检验。2组各时间点的SIT结果比较采用重复测量资料两因素方差分析。结果 实验组大鼠去卵巢后第3个月时,体内雌二醇浓度低于对照组(t=-35.37,P<0.01),睾酮浓度低于对照组(t=-12.13,P<0.01)。2组各时期SIT检查未见泪液分泌减少、均未见角膜荧光染色。HE染色见实验组泪腺腺泡萎缩,排列紊乱,胞质内酶原颗粒明显减少。泪腺IL-17A表达量2组比较实验组高于对照组(免疫组化法:t=7.56,P<0.01;Western Blot法:t=20.90,P<0.01)。余各因子表达量实验组也均高于对照组(免疫组化法:IL-1β:t=13.71,P<0.01;IL-6:t=13.92,P<0.01;TNF-α:t=6.11,P<0.01。Western Blot法:IL-1β:t=16.93,P<0.01;IL-6:t=12.46,P<0.01;TNF-α:t=14.47,P<0.01)。结论 大鼠去卵巢3个月时性激素水平降低,未见明显眼表损害。但泪腺中炎症因子IL-17A、IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的表达增加。
【关键词】 去卵巢大鼠; 泪器; 白细胞介素17A; 白细胞介素1β; 白细胞介素6; 肿瘤坏死因子α
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-845X.2014.09.003
作者单位:215006 眼科
通信作者:张晓峰,Email:zhangxiaofeng@suda.edu.cn
Expression of IL-17A in the lachrymal glands of rats after ovariectomy
Zhong Lei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Xia Jing, Xia Wei, Sun Zhengtai, Wang Yingming. Department of Ophthalmology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
Corresponding author:Zhang Xiaofeng,Email:zhangxiaofeng@suda.edu.cn
【Abstract】 Objective To study the expression of inflammatory factors IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in the lachrymal glands of ovariectomized rats when the level of sex hormones changes. Methods This was an experimental study. Twenty healthy female SD rats were divided randomly into a control group (n=10) and an experimental group (n=10). Ovariectomy was performed on the experimenal group, while a sham operation was performed on the control group. A Schirmer Ι test (SIT) and corneal fluorescence staining were performed on both groups before surgery and at 1, 2, and 3 months after surgery. The results were analyzed with the repeated measurement ANOVA. Acinar cells from the lacrimal glands were examined by HE staining. At the 3rd month, the concentrations of estrogen and androgen were measured by radiation immunoassay detection and were analyzed with independent sample t tests. The expressions of IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α were analyzed by immunohistochemical and Western blot methods with independent sample t tests. Results The concentration of estrogen and androgen in the experimental group decreased compared with the control group (t=-35.37, -12.13, P<0.01). There were no differences between the control group and the experimental group for the SIT and corneal fluorescence staining at each time point (P>0.05). HE staining showed that the enzymes of the original particles in the lachrymal cells were significantly reduced while acinar atrophy and cell arrangement disorder were observed in the experimental group. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the expression of inflammatory factors in the lachrymal glands was significantly higher in the experimental group compared with those in the control group (A value: IL-17A: t=7.56, P<0.01, IL-1β: t=13.71, P<0.01, IL-6: t=13.92, P<0.01, TNF-α: t=6.11, P<0.01). Western blot analysis showed that the expression levels of inflammatory factors in the lachrymal glands were significantly higher in the experimental group compared with those in the control group (A value: IL-17A: t=20.90, P<0.01, IL-1β: t=16.93, P<0.01, IL-6: t=12.46, P<0.01, TNF-α: t=14.47, P<0.01). Conclusion The levels of estrogen and androgen in the experimental group dropped at the 3rd month postoperatively but there were no obvious clinical signs found on the ocular surface. The expression of inflammatory factors, such as IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α, increased in the lachrymal glands of ovariectomized rats.
【Key words】 Ovariectomized rat; Lachrymal apparatus; Interleukin-17A; Interleukin-1β; Interleukin-6; Tumor necrosis factor-alpha