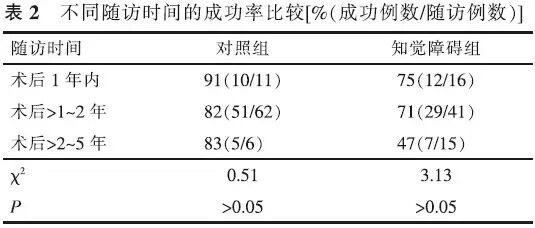
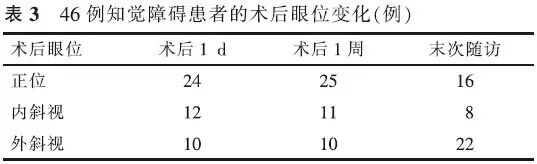
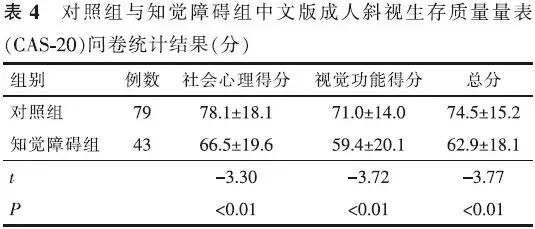
【摘要】 目的 研究伴有知觉障碍的成人斜视患者斜视矫正术后的远期效果,探讨术后不同时间的眼位变化、成功率及手术效果的影响因素。方法 回顾性病例对照研究。分析72例伴有单眼或双眼知觉障碍(BCVA<0.3)的成年斜视患者(知觉障碍组)斜视矫正术后远期的眼位、双眼视功能、生存质量状况,并与同期手术的79例无明显知觉障碍的患者(对照组)进行对照。数据采用独立样本t检验、χ²检验、秩和检验、logisitic回归分析。结果 术后2年内,对照组和知觉障碍组的成功率差异无统计学意义(χ2=1.97,P>0.05);末次随诊时对照组66例(84%)成功,知觉障碍组48例(67%)成功,2组成功率差异有统计学意义(χ2=6.14,P<0.05)。24例不成功的知觉障碍患者中,22例欠矫,2例过矫。知觉障碍组术后3例有部分立体视功能;对照组术后17例有正常立体视功能,17例有部分立体视功能;2组术后立体视功能水平差异有统计学意义(χ2=31.34,P<0.01);知觉障碍组术后生存质量评分(社会心理得分、视觉功能得分、总分)显著低于对照组(t=-3.30、-3.72、-3.77,P<0.01)。知觉障碍组患者术后成功率与年龄、偏斜程度和随诊时间无明显相关性。结论 约有2/3的伴有知觉障碍的成人斜视患者术后远期效果成功,其手术后远期的眼位、双眼视功能和生存质量水平均低于无明显知觉障碍者。
【关键词】 知觉障碍; 斜视手术; 治疗效果; 生存质量
Study of the long term effects of corrective surgery in adult strabismus patients with visual impairment
Ji Zhouduo*, Yu Xinping, Yuan Siqi, Yu Huanyun, Xu Meiping. * Eye Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, China
Corresponding author: Yu Xinping, Email: yu-xinping@163.com
【Abstract】 Objective To evaluate the long term effect of corrective surgery in adult strabismic patients with visual impairment; to study the stability of postoperative alignment and factors that influence it. Methods This was a retrospective clinically controlled study of the alignment, binocular vision, ocular movement and quality of life in 72 adult strabismic patients with visual impairment (BCVA less than 0.3 in one or both eyes). These patients were compared to 79 patients without visual impairment. Data were analyzed using an independent samples t test, χ² test, rank sum test and logisitic regression analysis. Results There was no significant difference in the success rate between the two groups within 2 years after surgery (χ2=1.97, P>0.05). Forty-eight (67%, 48/72) and sixty-six (84%, 66/79) were defined as ″successful″ at the last follow-up in the visually impaired group and control group, respectively. The difference was significant(χ2=6.14, P<0.05). Of the 24 patients defined as ″not successful″ in the visually impaired group, 22 cases were under-corrected and 2 cases were over-corrected. Three patients and 34 patients achieved normal or partial stereoacuity in the visually impaired and control groups, respectively. The difference in stereoacuity between the two groups was significant (χ2=31.34, P<0.01). The scores from the quality of life questionnaire were lower in the visually impaired group than in the control group (t=-3.30, -3.72, -3.77, P<0.01). Conclusion Approximately two in three patients with visual impairment can achieve long-term successful outcomes with corrective surgery. However, alignment stability, binocular vision and quality of life were worse in patients with visual impairment than in those without visual impairment.
【Key words】 Perceptual disorders; Corrective surgery; Therapy outcome; Quality of life
DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-845X.2015.04.002
作者单位:325027 (姬周朵、余新平、余焕云、许梅萍,姬周朵为研究生,现在郑州市第二眼科);341000 赣州,赣南眼科(袁思奇)
通信作者:余新平,Email:yu-xinping@163.com